Geared Aerodynamic Pan and Tilt
| |
This page or section is under construction and will change going forward.
Questions or Comments? Please contact the Wiki administrator |
Contents |
|
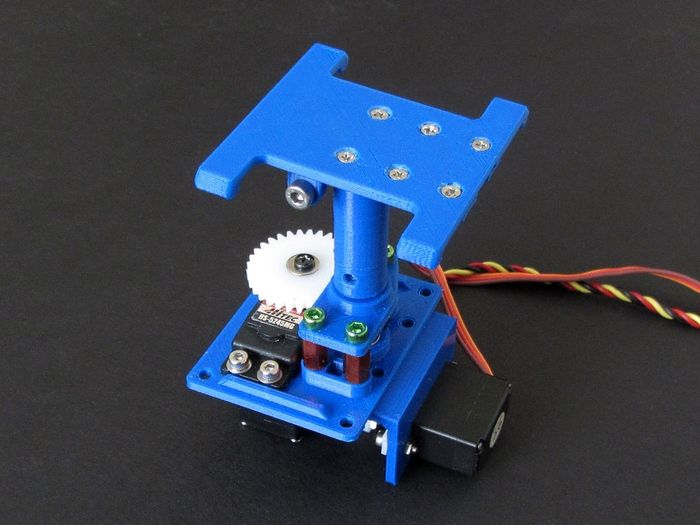
| Aerodynamic and Accurate! |
Introduction
Having designed and released a pile of different Pan and Tilt units I decided to try and make something a little different. I came up with a list of simple design goals that were based on requests and experiences with other PnT's. The list then, in (my) order of importance is:
- Lighter and Faster than my HD Pan and tilt which is around 100g
- - New weight is ~80g with the components shown here
- Is smooth and precise with excellent centering
- - With a new, fully programmable digital Hitec HS-5245MG servo, it is extremely smooth and centers beautifully
- Is more aerodynamic
- - Now with both servos mounted below the deck, it is very aerodynamic
- Can be made from off-the-shelf components
- - All but one component is made from standard off-the-shelf parts (see text)
- Rotates 360° or more
- - Rotation can be programmed from 236° to 398°
- Tilts down 50 degrees or more
- - Tilts down 42° (see text)
As you can see I came pretty close to hitting most of these goals. For the two I missed a little:
- - The one component which could not easily be made from off the shelf parts is the aluminum gear shaft which I turned in a mini lathe. There is more information on this in the build section.
- - The tilt-down spec can and will likely change. The cost for increasing tilt-down is the assembly gets taller, a little harder to make smooth and slightly less aerodynamic. I was happy with 42° as this is more than enough for the planes I plane to use it on.
NOTE Apologies to all followers in Europe and Australia! The components selected started with a new (awesome) drive gear from ServoCity.com which I know can be very hard to find outside the US. This new drive gear comes with the Hitec C1 spline already molded in which made the design and subsequent build much easier. Of course this also means the gear shaft and bearings are also imperial dimensions.
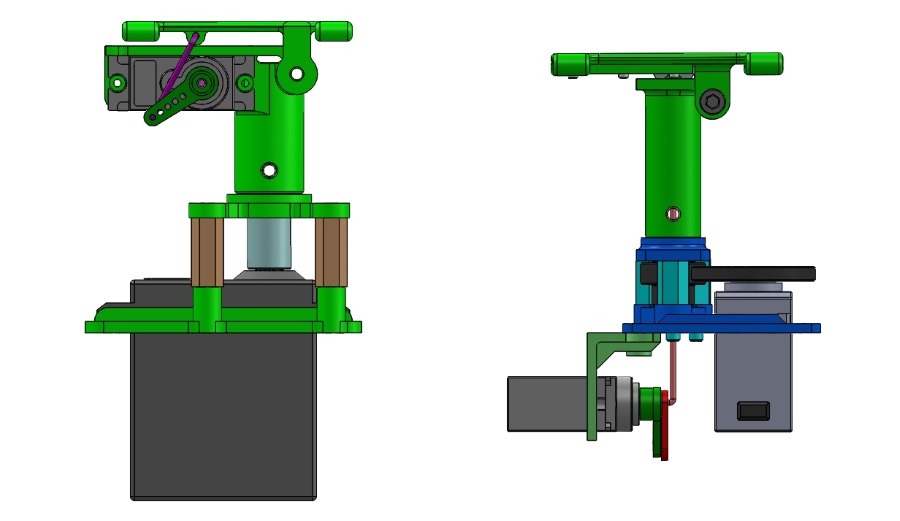
The new unit has a lower profile than the HD unit and needs a smaller through-deck hole:
|
| HD and Aerodynamic Pan and Tilts |
Configurations
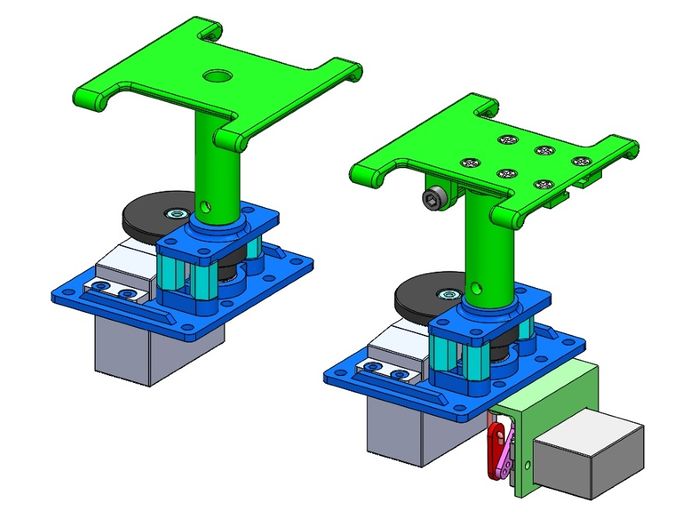
For this project I decided to keep it simple so there is only one pan-only setup and one tilt setup. I will likely add a custom RunCam Split deck like I have done on my Offset Pan and Tilt in the future.
|
| Pan-only and Tilt decks |
Notes on Standard Configuration
- TBA
The Build
On any project such as this, understanding the work scope and finding the resources needed is a key to success. For the full tilt version there are 6 3D print parts that require some detail work and one aluminum gear shaft that will require some machining.
Parts and Specifications
The parts shown here are what was used on the unit when released. This list can change over time as I look for ways to improve it.
Print Parts
- Base Plate
- Bearing Support Plate
- Tilt Servo Mount Bracket
- Tilt Turret
- Tilt Deck
- Tilt Deck Slide Covers
- Pan Deck
- Printable STL files are at the bottom of this page
Off the Shelf Parts
- 2x Dubro #107 1/2A Control Horns (one pair)
- 1x Dubro #109 2-56 Spring Steel Kwik-Link Clevis
- 1x Dubro #172 2-56 Threaded Rod
- 1x Pushrod Linkage Stopper D2.1mm
- 1x ServoCity #RSA32-2HS-26 32 pitch/26 tooth Acetyl Servo Gear - C1 Spline
- 1x ServoCity #SPBD32-34-16 32 pitch/16 tooth Acetyl Plain Bore Gear
- 2x ServoCity #535018 .250"ID x .375"OD x .125"L Non-Flanged Ball Bearing w/Dual Shield
Servos
- Pan - Hitec HS-5245MG digital programmable Mini Servo (32g)
- Also needed - Hitec HPP-21 PC Digital Servo Programmer
- Tilt - Corona DS929MG digital micro servo (14.1g)
- NOTE: This project was designed specifically around the two servos shown
Hardware
- 4x M2.5x6mm Machine screws, Stainless Steel
- 4x M2.5 Flat Washers, Stainless Steel
- 8x M3 x 6mm Machine Screw, Aluminum
- 3x M3 x 10mm Stand-off, Aluminum
- 1x M3 x 30mm Machine Screw, Stainless Steel
- 1x M3 Nylok Nut, Stainless Steel
- 2x M2 x 8mm Machine Screw, Stainless Steel
- 2X M2 Hex Nut, Stainless Steel
- 2x M2 x 4mm Machine Screw, Stainless Steel
- 6x M2 x 5mm Flat Head Machine Screw, Steel
- 1x M2 Flat Washer, Stainless Steel
Mechanical Specifications
- Total weight with all hardware shown - 89 grams
- Pan rotaion - 236 - 398 degrees
- Tilt range - 0-42 degrees (down)
3D Parts
It is important here to makes sure your printer is calibrated for the filament you have selected as there are three critical dimensions to hit for a successful build:
- The distance on the base plate between the two gear centers
- The bearing hole diameters
- The gear shaft fit into the turret base
If you don't know whether your printer is calibrated, create or download a 20mm test cube, print it, and measure the results. If the test cube is within 0.25% (19.95mm to 20.05mm))or better of 20mm, then you are OK. If not, go through the calibration process on your printer or try scaling the print to fit.
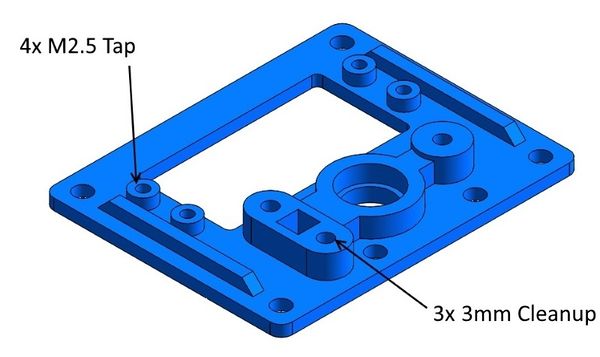
Base Plate
The base plate and bearing support plate are designed so the ball bearing just pushes in. If the bearing is to tight, a dremmel sanding tube can be used to gently open it up. If the bearing hole is too loose, small strips of cellophane tape can be used to tighten it up.
The base plate needs the 4 servo mount holes tapped to M2.5 and bearing support holes cleaned up to 3mm. An alternative to the M2.5 tap is to use four M2 x 8mm machine screws with nuts and large flat washers.
|
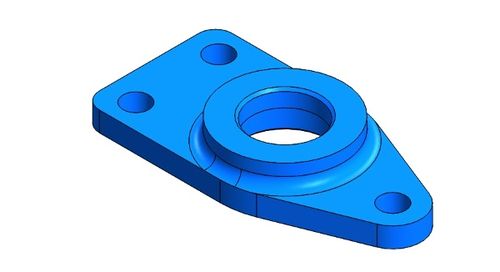
Bearing Support Plate
The support plate needs the three 3mm holes cleaned up with a 3mm drill bit and the bearing bore cleaned and checked for fit.
|
Turret Base
The Turret needs 4 holes cleaned up to 3mm and the bottom interface hole cleaned up to .250" (6.35mm). It is important this is a snug fit (but not too tight!)

|
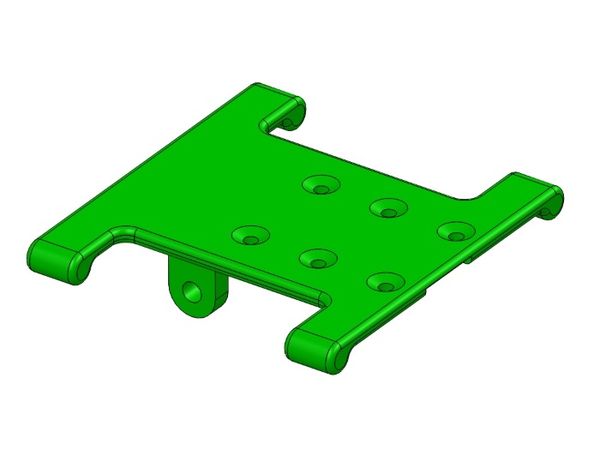
Tilt Plate
The Tilt plate needs 6 holes cleaned up for the M2 x 5mm flat head screws and the two pivot holes cleaned up to 3mm. Additionally, make sure the slide channel is smooth with no bumps or print berries.
|
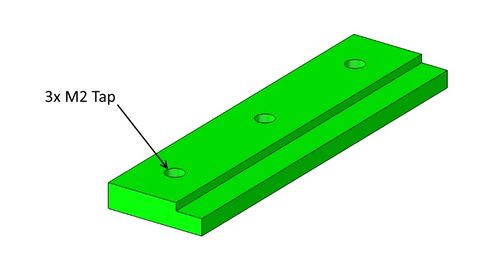
Slide Covers
The slide covers need their 3 holes tapped to M2 -or- you can glue these plates on.
|
Mechanical Parts
Here you will see the "made from off-the-shelf" parts and the (machined) gear shaft.
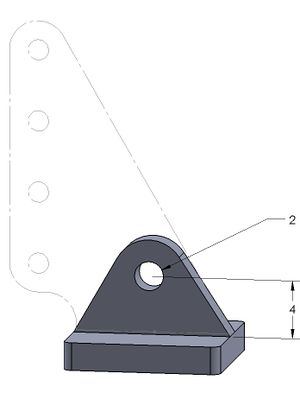
Slide Block
The slide block is made from a nylon Dubro 1/2A control horn. It has a 2mm hole drilled into it at 4mm above the bottom plate and the rest of the top material cut away. The base plate is 1.9mm thick and should have the edges slightly scraped for any rough bits.
|
Connecting Rod & Steel Clevis
The connecting rod is made from a piece of "end threaded" 2-56 control wire. The threaded end is cut so 1/4" (~6mm) of the threads are left and the length is then trimmed to 2-5/16" (~59mm) . Cleanup the end with the threads so when it is threaded into the steel clevis it spins easily. This threaded connection forms the basis for the control links ability to spin with the rotation of the unit.

|
Servo Control Link
The servo control link is also made from a Dubro control horn. The 1/2A size will work (shown below) by trimming away the material around the three holes. A longer control horn or other material can also be used with the two outside hole centers at 0.385" (9.8mm) to 0.410" (10.4mm) apart.
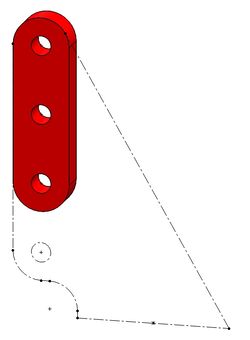
|
Servos
The Pan servo, a Hitec HS-5245MG was selected because of its programmability, speed and great accuracy. It is also 23g lighter, smoother and faster than the GWS S125-1T servo I use in my HD Pan and Tilt. To program the servo you will need to get the Hitec HPP-21 digital programmer (~$27). With this tool you can change the servos speed, endpoints, center, max rotation and deadband (yes, this servo is a little pricey).
The tilt servo is a Corona digital DS-929MG which I chose because I have a pile of them and they have always worked well for me. Just about any "9 gram" size servo can be used although you will likely have to make more adjustments to linkage parts, etc. You might also have to "adjust" or change the servo mount.
Why Digital
I use digitals now almost exclusively. They are better at rejecting spurious RF noise than analogs and, obviously, you can find them programmable. As far as digital servos injecting noise into the planes control system, I have found that as long as you carefully route wires, braid and twist and use ferrite rings there is no issue with this.
Assembly
Here is a 3D image of assembly parts partially exploded:
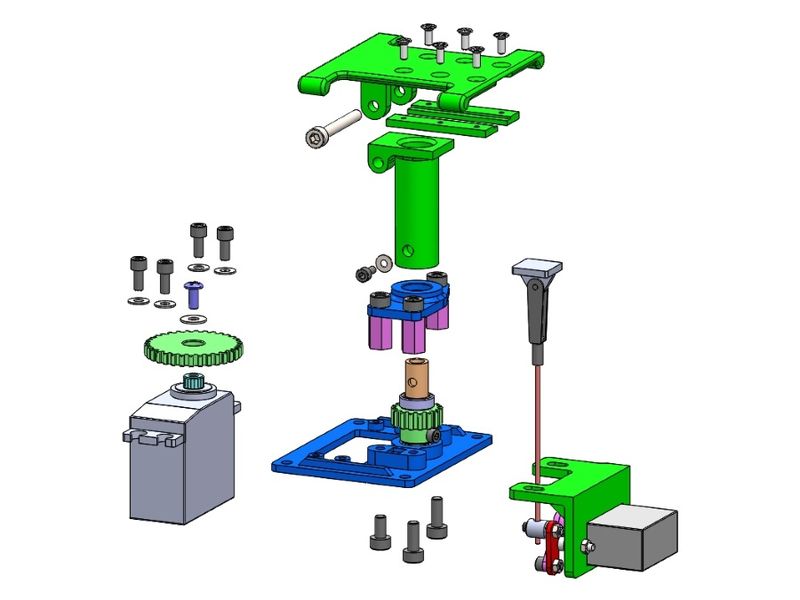
|
A Video Sample
Here is the teaser video I did for this project. I'll add an in-flight sample at a later date.
|
Imagined and Real |
See Also
Project 3D Print Files
The following are the 3D print ZIP files used in this specific build. For more versions and information, please see my Thingiverse postings here:
Mark_q Thingiverse Designs
Where to buy the parts
- For the bearing and servo coupler -
- For the GWS S125-1t 25t servo -
- Global - GWS S125-1t Servo
Comments? Questions?